High School & Postsecondary
Early College Credit
Overview
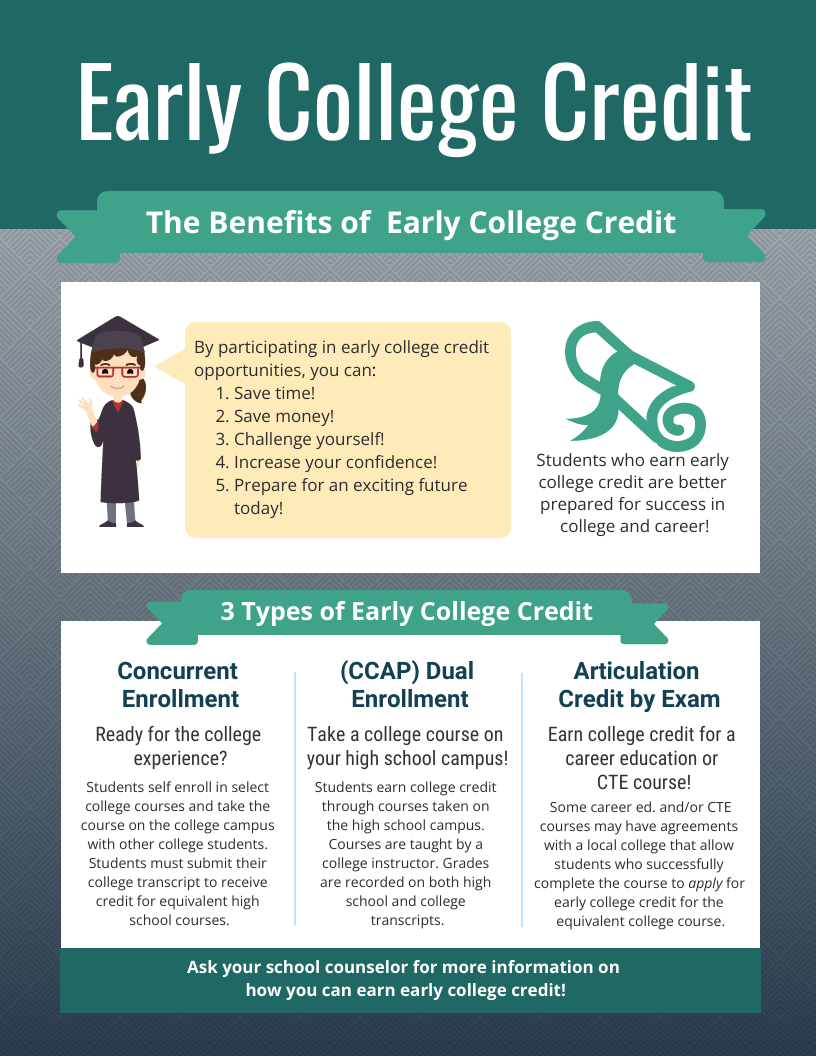
Early College Credit is an umbrella term for the various ways that high school students can earn college credit prior to graduation. There are three main routs:
- Dual Enrollment
- Articulation Credit-by-Exam
- Concurrent Enrollment
Articulation Credit by Exam
Dual Enrollment
The term dual enrollment is used when high school, Adult School, and noncredit students are enrolled in their respective institutions and in a community college credit-bearing course at the same time. At the college, these students are known as “special part-time” or “special full-time” students. Dual enrollment is sometimes used interchangeably with concurrent enrollment, but they are different. Dual enrollment involves college courses scheduled for and made up of high school (or Adult School) students whereas concurrent enrollment involves students acting individually to apply to take college courses at college. Dual enrollment includes dual enrollment through College and Career Access Pathways (CCAP) Partnership Agreements, non-CCAP dual enrollment, and SB 554, the legislation enabling dual enrollment for Adult School and noncredit students.
Join the Regional Dual Enrollment Community of Practice!